Artificial Intelligence (AI) has played a significant role in various aspects of the Chandrayaan 3 mission, from planning and navigation to data analysis and communication. Here is how AI facilitated ISRO to achieve the mission.
The head of ISRO, Chairman S Somnath, has recently revealed a groundbreaking technological advancement that has the potential to revolutionize lunar missions, and how AI facilitated ISRO.
Advertisement
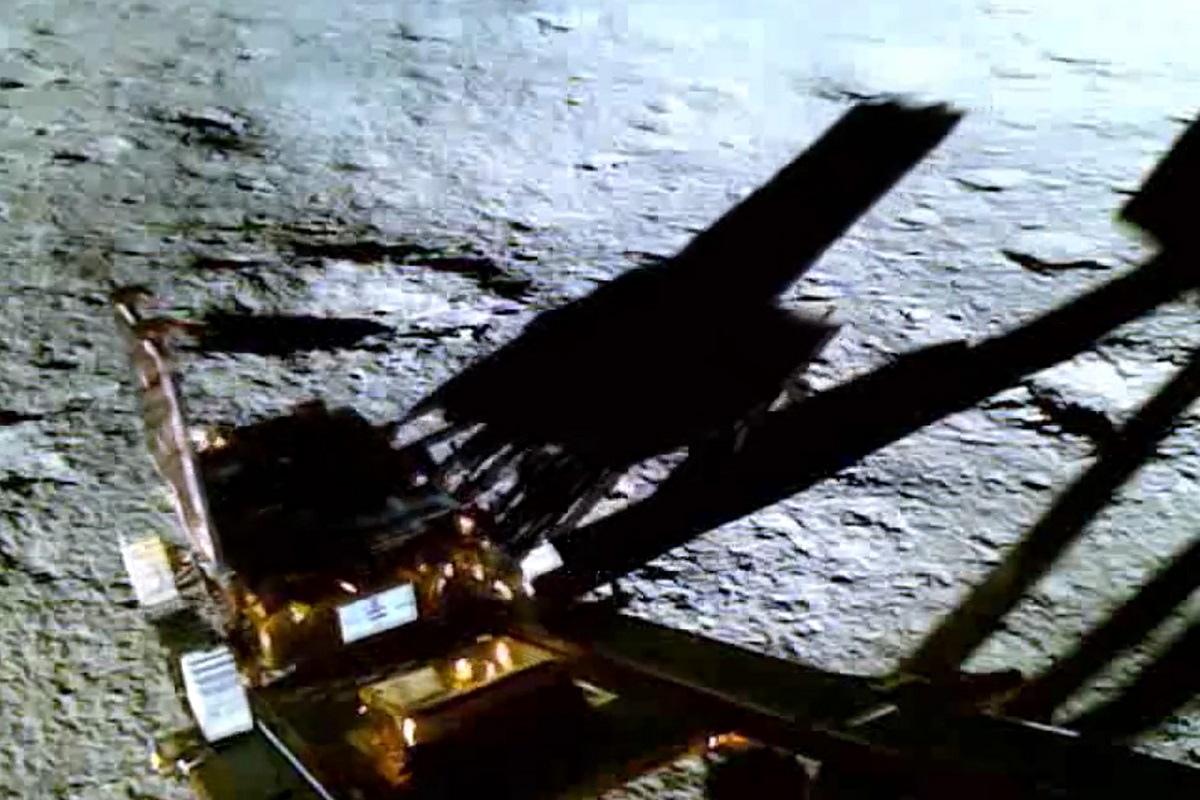
This advancement involves a sophisticated sensor array, which incorporates velocimetry and altimeters. These precision instruments serve a pivotal role in collecting vital information concerning the lander’s velocity and altitude during descent.
In parallel, an array of cutting-edge cameras, specifically designed for hazard avoidance and inertia-based visual tracking, was deployed. These cameras were strategically positioned to capture crucial images of the lunar surface and the surrounding environment.
The true innovation lies in the integration of advanced computer algorithms. These algorithms, harnessing the power of artificial intelligence, skillfully amalgamate the data streams from the sensor array and cameras.
The outcome is a comprehensive, high-resolution image that not only provides a visual representation of the lunar landscape but also pinpoints the precise coordinates of the lander. This level of precision is indispensable for ensuring a safe and accurate lunar landing, marking a significant stride in lunar exploration technology. Following are some of the facets that have played a significant role in various aspects of the Chandrayaan 3 mission’s success due to artificial intelligence.
1. Autonomous Navigation:
AI algorithms helped the rover autonomously navigate and avoid obstacles on the moon’s surface. This is crucial for landing safely and moving around efficiently.
2. Robotic Exploration:
The AI-powered Pragyan rover has already started collecting data in this lunar exploration. It uses machine learning to adapt to the lunar environment, identify interesting geological features, and make decisions on where to explore.
3. Predictive Maintenance:
AI can analyze data from spacecraft systems to predict when components are likely to fail, allowing for proactive maintenance and reducing the risk of mission failure.
4. Data Analysis:
AI processes and analyzes the vast amounts of data collected during a mission. This includes analyzing images, spectroscopic data, and geological data to make scientific discoveries.
5. Predicting Space Weather:
AI can help predict space weather conditions, such as solar flares or radiation storms, which can impact the safety and the functionality of the lander.
6. Mission Planning:
AI has assisted in optimizing mission planning, taking into account factors like fuel consumption, orbital dynamics, and communication windows.
7. Data Transmission:
AI has improved data transmission and storage efficiency, ensuring that valuable scientific data reaches Earth intact and in a timely manner.
8. Environmental Monitoring:
AI has helped monitor the moon’s environment for changes over time, such as temperature fluctuations, seismic activity, or the presence of water ice.