Aditya L1 Solar Mission: Days after the historic success of Chandrayaan 3, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is all set to launch India’s first space-based observatory class mission Aditya L1 to study the Sun. The Aditya L1 spacecraft will be launched from Andhra Pradesh’s Sriharikota on Friday, September 2. ISRO said that the Aditya L1 spacecraft will be placed in a halo orbit around the Lagrange Point L1 of the Sun-Earth system.
According to ISRO, Aditya L1 will be able to continuously view the Sun without any obstructions from the Lagrange Point L1. This point between the Sun and the Earth will also give an advantage to the spacecraft to observe the solar activities and their effect on space weather in real-time, the agency said.
Advertisement
Aditya L1 spacecraft will carry seven payloads – Visible Emission Line Coronagraph(VELC), Solar Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (SUIT), Solar Low Energy X-ray Spectrometer (SoLEXS), High Energy L1 Orbiting X-ray Spectrometer(HEL1OS), Aditya Solar wind Particle Experiment(ASPEX), Plasma Analyser Package For Aditya (PAPA), and Advanced Tri-axial High-Resolution Digital Magnetometers.
ISRO said that these payloads will help the observatory class spacecraft to observe the photosphere, chromosphere, and the outermost layers of the Sun (the corona) using electromagnetic particle and magnetic field detectors.
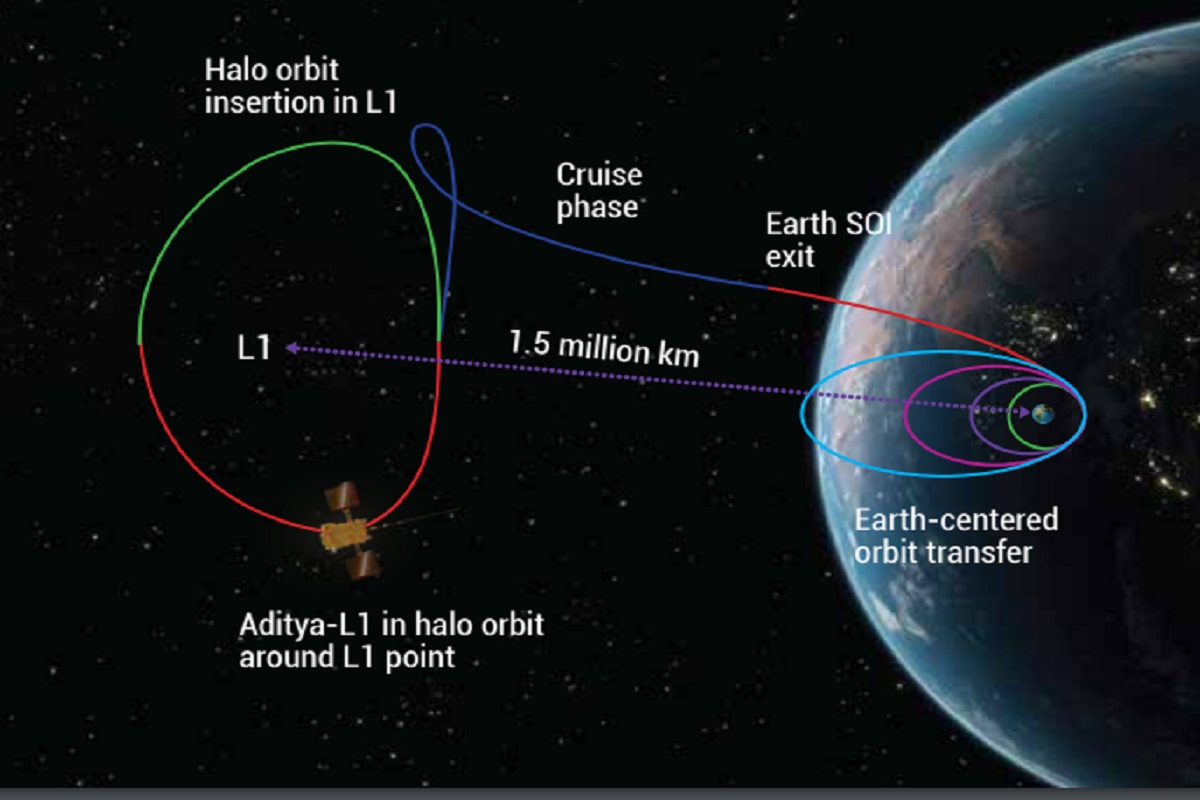
Aditya L1’s journey from Earth to Lagrange Point L1
The journey of the Aditya L1 spacecraft to the Lagrange Point L1 will be 15,00,000 km from the Earth and it will take 125 days to cover the distance. The staggering 1.5 million KM journey of Aditya L1 will not be an easy ride and involve a lot of risks.
According to ISRO, the spacecraft will be initially placed in a low-earth orbit before being launched towards the Lagrange Point L1. Once in the low earth orbit, the orbit will be made more elliptical, and on-board propulsion will launch the spacecraft towards Lagrange Point L1.
In other words, Aditya L1 will be launched from Sriharikota toward the low-earth orbit and then from there, it will be launched again towards the L1.
The spacecraft, ISRO said, will exit the Earth’s gravitational Sphere of Influence, and once out of it, the “cruise phase” will be initiated. This “cruise phase” maneuver will guide the spacecraft towards a large halo orbit around the L1 point.
Click on the highlighted part to learn more about the Lagrange Point L1 and Aditya L1’s mission objectives.